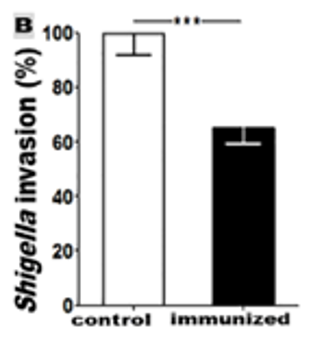
Dr. Zhang from the University of Illinois has developed a promising candidate protein for a vaccine against Shigellosis, an infectious gastrointestinal disease caused by Shigella bacteria. The protein is a multiepitope fusion antigen (MEFA), incorporating virulence factors which are conserved across multiple Shigella serotypes.
When administered to animals, this fusion protein induces protection against Shigella epithelial cell invasion. Since virulence factors from multiple serotypes are included in the fusion protein, this protection can be extended to the various Shigella serotypes.