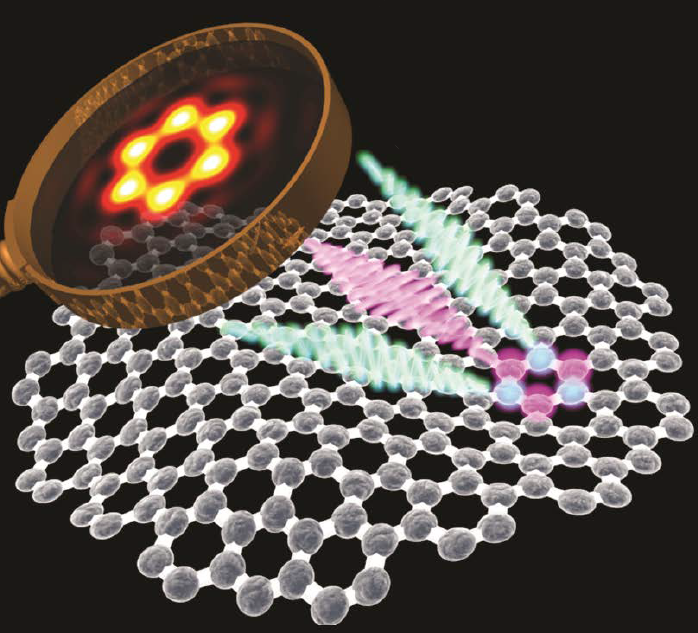
The development of unlimited resolution imaging systems based on the fundamentally odd-symmetric polarization topology which breaks the 145-year-old law of Abbe’s resolution limit. With this technology, two objects separated by an arbitrarily small gap can be distinguished using a conventional far-field imaging system that has an arbitrarily low numerical aperture of the objective lens. The system allows imaging of nanoparticles and nanostructure which was previously not achievable by conventional optic microscopes.